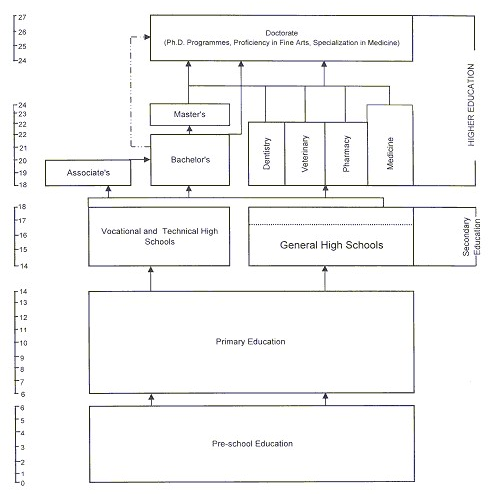
The basic structure of the Turkish National Education system consists of four main stages as pre-school education, primary education, secondary education and higher education.
Pre-school education consists of non-compulsory programmes whereas primary education is a compulsory 8-year programme for all children beginning from the age of 6. The secondary education system includes "General High Schools" and "Vocational and Technical High Schools".
Higher education is defined as all post-secondary programmes with duration of at least two years. The system consists of universities (state and foundation) and non-university institutions of higher education (police and military academies and colleges). Each university consists of faculties and four-year schools offering Bachelor's level programmes, the latter with a vocational emphasis, and two-year vocational higher schools offering short cycle (Associate's) level programmes of a strictly vocational nature.
The Higher Education Law No. 2547 is the main law, which governs the higher education in Turkey. All universities (both state and foundation) are subject the same law and regulations/rules. All state and foundation universities are founded by Law.
Admission to higher education is based on a nation-wide Student Selection Examination (ÖSS). The examination is held once a year and is administered by the Student Selection and Placement Center (ÖSYM). Candidates gain access to institutions of higher education based on their composite scores consisting of the scores on the selection examination and their high school grade point averages.
Graduate level of study consists of the Master's Degree (Yüksek Lisans Diplomasi) and the Doctoral Degree (Doktora Diplomasi). There are two types of Master's programmes: with and without a thesis. The Master's programmes with a thesis consist of a minimum of seven courses, one seminar course, and thesis. The duration of the Master's programmes with a thesis is two years. Non-thesis Master's programmes consist of a minimum of 10 courses and a semester project. The duration of the non-thesis Master's programmes is one and half years. Doctoral programmes have a duration of four years which consists of completion of courses, passing a doctoral qualifying examination, and preparing and defending a doctoral dissertation. Medical specialization programs are equivalent to doctoral level programmes and carried out within the faculties of medical schools with hospitals.
The Higher Education System is regulated by the Council of Higher Education (Yüksek Öğretim Kurulu-YÖK). Established in 1981, the Council regulates the activities of higher education institutions with respect to research, governing, planning and organization.